DL M12: Machine Translation (Meta)
Module 12 of CS 7643 - Deep Learning @ Georgia Tech.
Introduction
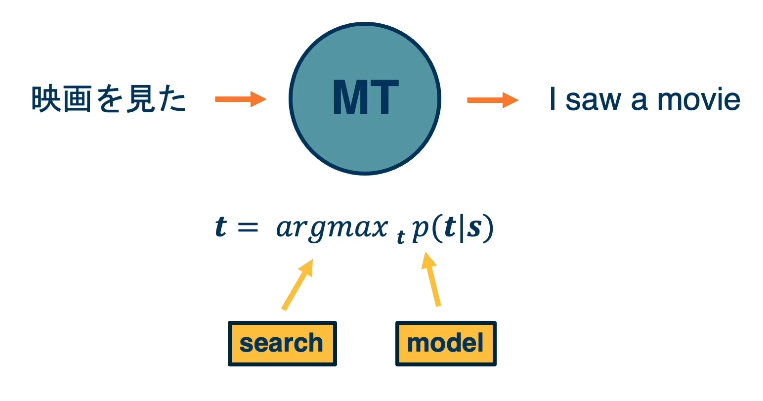
Machine Translation is a natural language processing task which involves mapping text from a source language to a target language.
Neural Machine Translation
Difficulties of Machine Translation
Why is machine translation a difficult problem?
1) Many different correct translations for a typical input sequence. 2) Language is ambiguous / depends on the context. 3) Different languages have different structure, implications, etc.
Machine Translation as an NLP Problem
We can frame translation as the following machine learning problem:
That is, given a source sequence $s$, we are interested in modeling the conditional probability distribution over our target sequences $t \in T$. We can then generate a prediction by taking the argmax over this estimated distribution $\arg \max_t \Pr(t|s)$.
Machine translation typically uses a sequence-to-sequence model implemented via an encoder-decoder architecture. The major model types include RNNs (typically LSTMs), CNNs, and transformers.
Beam Search
Unfortunately, the number of possible target sequences $t \in T$ is intractable - there are simply too many possible predicted translations for us to explore them all. We can instead use methods to approximate the true argmax over the full target distribution.
Beam Search is an algorithm which searches exponential space in linear time.
- Beam size $k$ determines width of search.
- At each iteration, extend each of $k$ hypothesis predictions by one token.
- Top $k$ most probable sequences then become the hypotheses for the next step.
Inference Efficiency
Inference refers to the process of generating prediction(s) using a machine learning model. There are certain model characteristics which can influence inference efficiency.
- Autoregressive inference (step-by-step computation over long sequence).
- Output projection $|V| \times L \times k$
- Deeper models
We can improve inference efficiency via a number of strategies:
- Vocabulary Reduction: constrain vocabulary based on probability of seeing certain words given input sequence. ex: use training data to estimate probability of observing words given sequence.
- Sub-word Models: break up words based on frequency; strategies include Byte-Pair Encoding.
- Layer Drop: probabilistically select layers to prune at inference time.
- Specialized Hardware: for batched ML systems, use parallel architectures to take advantage of parallel computation.
- Quantization: perform inference in a lower precision domain (ex:
float32$\rightarrow$float8). - Non-autoregressive models: instead of using model which predicts sequentially, predict entire sequence in one iteration.
(all images obtained from Georgia Tech DL course materials)